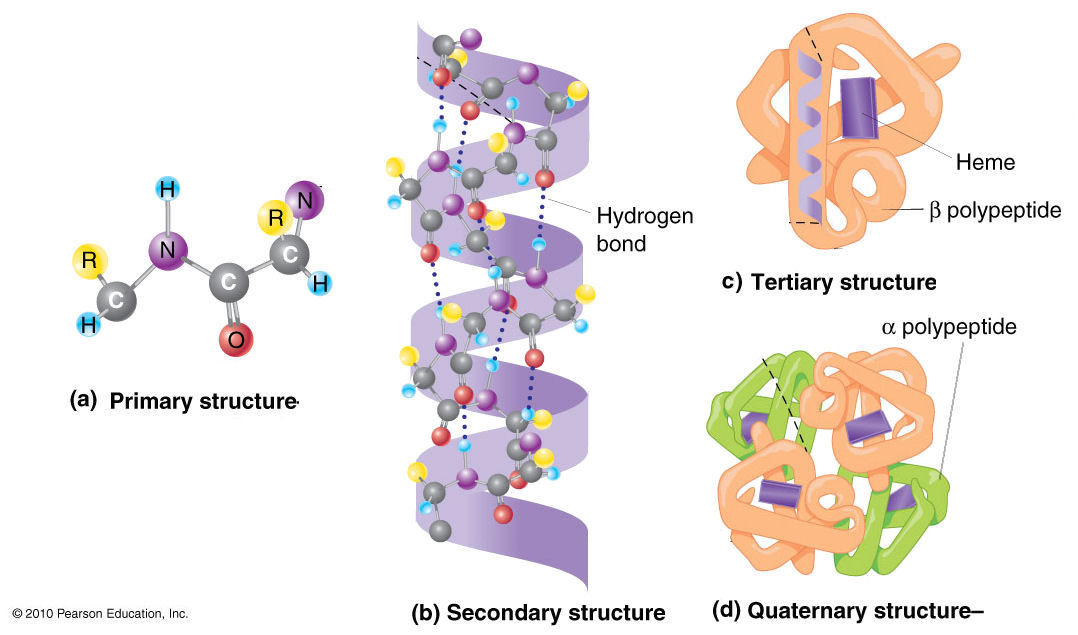
Using Hemoglobin as an Example Describe Quaternary Protein Structure
What are commonly occuring examples of proteins with more than one chain. Many proteins are found in aggregated states and hence have quaternary structure.

Quaternary Structure Of Protein What Is Quaternary Structure Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Consisting of four.

. In hemoglobin one protein binds to oxygen while another binds carbon dioxide. In hemoglobin one protein binds to oxygen while. Tertiary Structure is the final shape of an entire amino acid chain.
Define primary structure and describe how ti may be deduced in the laboratory. Two of the subunits are alike and two are different. The quaternary protein structure involves the clustering of several individual peptide or protein chains into a final specific shape.
For example hemoglobin has a molecular weight of 64000 and is composed of four subunits each of molecular weight 16000. Linear string of spheres spheres arranged one upon the other in the form of a cube or plate is the architecture of a protein which is referred as the quaternary structure of a. Chemists describe symmetry through the use of mathematical symmetry operations and elements which find.
However hemoglobins quaternary structure sets it apart. Many proteins consist of more than one subunit. Quaternary Structure refers to the structure of a protein macromolecule formed by interactions between multiple polypeptide chains.
Can the chains be identical. Individually each alpha helix is a secondary polypeptide structure made of amino acid chains. Those that consist of more than one polypeptide chain.
Major examples include insulin hemoglobin and most enzymes. Hemoglobin occupies the fourth or quaternary level of protein structure. The common oligomer subunits are either dimer trimers tetramer pentamer and so on.
The quaternary structure involves the arrangement of multiple polypeptide chains within the same molecule. Each chain is called a what. Hemoglobin found in the blood is an iron-containing protein that binds oxygen molecules.
The polypeptide subunits associate in a specific order to form the oligomer. Hemoglobin While many proteins are biologically active as tertiary structures some proteins require two or more tertiary structures to be biologically active. The manner in which these individual folded polypeptides or subunits are arranged with respect to each other eg.
In collagen 3 polypeptides combine in a rope-like structure. Some proteins are an assembly of more than one polypeptide or subunits. Hemoglobin consists of two alpha and two beta monomers or protomers which assemble to produce the biologically relevant heterotetrameric protein.
The subunits in a quaternary structure must be specifically arranged for the entire protein to function properly. Quaternary protein structure differs between proteins. Enzymes composed of subunits with diverse functions are sometimes called holoenzymes in which some parts.
The functional three-dimensional shape of a protein complex made of multiple peptide chains. Quaternary Structure exists when more than one amino acid chain comes together to form a protein complex. Examples of proteins with quaternary structure include hemoglobin DNA polymerase ribosomes antibodies and ion channels.
Rogers PH Arnone A 1992 A third quaternary structure of human hemoglobin A at17-A resolution. If the final protein is made of two subunits the protein is said to be a dimer. Based on the subunits the quaternary structure is divided into the two.
Hemoglobin is an example of a protein with quaternary structure. Secondary Structures are the alpha helices and beta pleated sheets present in a folded proteins structure. An example of a protein with quaternary structure is hemoglobin.
We describe few examples of these variants that have mutations located at the surface of the protein heme pocket α1β2 or α1β1 interface or the hydrophobic interior that alter hemoglobin structure and affect its oxygen binding properties. The amino acids are in turn the primary structure of hemoglobin. Table 147 lists a few of the proteins that have quaternary structure.
Proteins associate with each other to form quaternary structures. Was the first protein the complete tertiary structure was determined by X-tray crystallography Has 8 α-helical region and no β-pleated Hydrogen binding stabilize the α-helical region Consist of a single polypeptide chain of 153 aacid residue and includes prosthetic group- one heme group Store oxygen as reserve against. The quaternary structure refers to the number and arrangement of the protein subunits with respect to one another.
Meanwhile hemoglobin made of 4 polypeptides forms a. This shape is directly related to the function of the protein. Based on its structural properties hemoglobin can be divided into two parts.
A protein part and a heme group. Each polypeptide chain is referred to as a subunit. A variety of bonding interactions including hydrogen bonding salt bridges and disulfide bonds hold the various chains into a particular geometry.
The quaternary structure refers to the subunit composition of the protein. The quaternary structure of a hemoglobin molecule includes four tertiary structure protein chains which are all alpha helices. The Quaternary Structure of Protein is consist of two or more polypeptide chains and are held together by noncovalent interactions hydrogen bonds ionic bonds and hydrophobic interactions Subunits may either function independently of each other or may work cooperatively as in hemoglobin in which the binding of oxygen to one subunit.
Using collagen and hemoglobin as an example describe quaternary protein structure. I believe that this is due in part to the addition of the heme or iron component of the protein. When a biologically active protein consists of two or more polypeptide chains or subunits the structural level is referred to as a quaternary structure.
Quaternary structure is the interaction of two or more folded polypeptides. One hemoglobin molecule is made up of four subunits and thus. If three subunits must come together the protein is said to be a.
Hemoglobin is a protein having a globular structure. Quaternary structure pertains to what proteins. Any alteration in the structure of the subunits or how they are associated causes marked changes in biological activity.
Many proteins require the assembly of several polypeptide subunits before they become active. Hemoglobin represents a protein that possesses a quaternary structure. DENATURATION OF PROTEINS Destruction of the secondary tertiary and quaternary structures of CHON leading to changes in its physical chemical and biological characteristics Involves transformation of a well-defined folded structure of a protein formed under physiological conditions to an unfolded state under non-physiological condition.

Quaternary Structure An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Quaternary Structure An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Using Hemoglobin as an Example Describe Quaternary Protein Structure"
Posting Komentar